JVM (Java Virtual Machine)
- Java Virtual Machine
- Internal Architecture of JVM
JVM (Java Virtual Machine) is an abstract machine. It is a specification that provides runtime environment in which java bytecode can be executed.
JVMs are available for many hardware and software platforms (i.e. JVM is platform dependent).
What is JVM
It is:
- A specification where working of Java Virtual Machine is specified. But implementation provider is independent to choose the algorithm. Its implementation has been provided by Sun and other companies.
- An implementation Its implementation is known as JRE (Java Runtime Environment).
- Runtime Instance Whenever you write java command on the command prompt to run the java class, an instance of JVM is created.
What it does
The JVM performs following operation:
- Loads code
- Verifies code
- Executes code
- Provides runtime environment
JVM provides definitions for the:
- Memory area
- Class file format
- Register set
- Garbage-collected heap
- Fatal error reporting etc.
Internal Architecture of JVM
| Let's understand the internal architecture of JVM. It contains classloader, memory area, execution engine etc. |
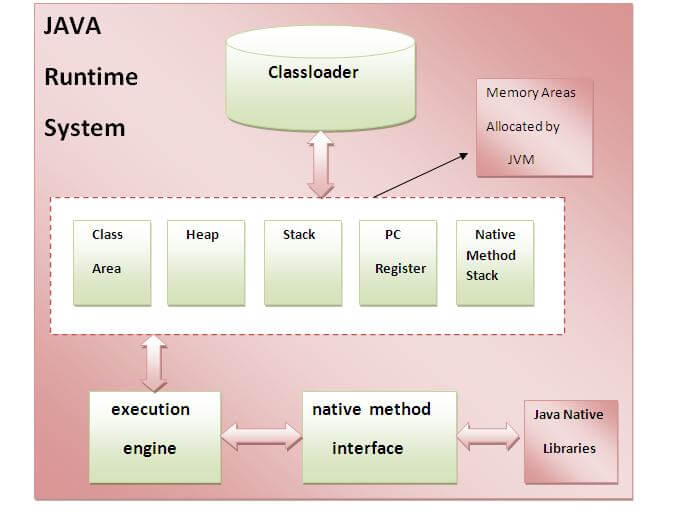
1) Classloader
Classloader is a subsystem of JVM that is used to load class files.
2) Class(Method) Area
Class(Method) Area stores per-class structures such as the runtime constant pool, field and method data, the code for methods.
3) Heap
It is the runtime data area in which objects are allocated.
4) Stack
| Java Stack stores frames.It holds local variables and partial results, and plays a part in method invocation and return. |
| Each thread has a private JVM stack, created at the same time as thread. |
| A new frame is created each time a method is invoked. A frame is destroyed when its method invocation completes. |
5) Program Counter Register
PC (program counter) register. It contains the address of the Java virtual machine instruction currently being executed.
6) Native Method Stack
It contains all the native methods used in the application.
7) Execution Engine
| It contains: |
| 1) A virtual processor |
| 2) Interpreter: Read bytecode stream then execute the instructions. |
| 3) Just-In-Time(JIT) compiler: It is used to improve the performance.JIT compiles parts of the byte code that have similar functionality at the same time, and hence reduces the amount of time needed for compilation.Here the term ?compiler? refers to a translator from the instruction set of a Java virtual machine (JVM) to the instruction set of a specific CPU. |
Comments
Post a Comment